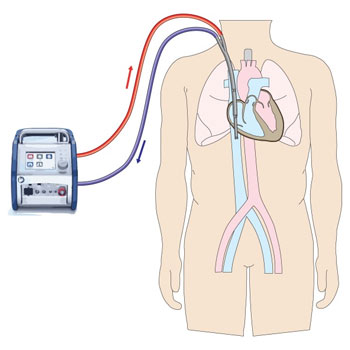
Extracorporeal support, often referred to in the context of cardiothoracic surgery, represents a critical advancement in medical technology that has revolutionized the management of complex cardiac and respiratory conditions. This technique involves temporarily taking over the function of the heart and/or lungs using external devices, allowing surgeons to perform intricate procedures that would otherwise be impossible. Here’s an in-depth look at what extracorporeal support entails, its types, applications, and its significance in modern medicine.
What are the types of extracorporeal support?
Extracorporeal support can be broadly categorized into two main types: extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) and cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB)
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation(ECMO)
ECMO is primarily used in cases where the patient's heart and/or lungs are severely compromised and cannot function adequately. It involves diverting blood from the body to an ECMO circuit where it is oxygenated and carbon dioxide is removed before being returned to the patient. This temporary support allows the heart and lungs to rest and recover, or it can sustain the patient's life during complex procedures such as heart transplantation or congenital heart defect repairs.
Cardiopulmonary Bypass (CPB)
CPB is utilized during cardiac surgeries to temporarily take over the function of the heart and lungs. It involves diverting blood away from the heart and lungs into a heart-lung machine, where it is oxygenated and pumped back into the body. This allows surgeons to operate on a still heart, making delicate procedures like coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and valve replacements feasible.
What are the applications in cardiothoracic surgery?
Extracorporeal support plays a pivotal role in numerous cardiothoracic surgical procedures, enabling surgeons to perform intricate interventions with enhanced precision and safety. Some key applications include
Complex Cardiac Surgeries
Procedures such as heart transplants, valve repairs, and congenital heart defect corrections often require the use of ECMO or CPB to maintain vital organ function during surgery.
Emergency Situations
In cases of cardiac arrest or severe respiratory failure, ECMO can provide immediate life support until the underlying condition is stabilized or treated.
Bridge to Recovery or Transplant
ECMO serves as a bridge to recovery by allowing the heart and lungs to rest and heal, or as a bridge to transplant by sustaining patients awaiting donor organs.
What is the significance of extracorporeal support in modern medicine?
The development and refinement of extracorporeal support technologies have significantly improved patient outcomes in cardiothoracic surgery. Key benefits include:
Improved Survival Rates
Patients undergoing complex procedures with extracorporeal support have higher survival rates compared to traditional methods.
Enhanced Surgical Precision
By temporarily replacing the function of the heart and lungs, surgeons can operate in a controlled environment, minimizing the risk of complications
Expanded Treatment Options
Extracorporeal support expands the range of conditions that can be effectively treated, offering hope to patients who previously had limited treatment options
Extracorporeal support represents a cornerstone of modern cardiothoracic surgery, enabling surgeons to undertake complex procedures with improved outcomes and patient safety. As technology continues to advance, the role of ECMO and CPB in managing cardiac and respiratory conditions will likely expand, further enhancing the capabilities of cardiovascular medicine.
By understanding the nuances of extracorporeal support, healthcare providers can better inform patients and their families about these critical technologies and their potential impact on treatment plans and outcomes. For further information or to consult with a specialist in cardiothoracic surgery, reach out to Dr Varun Cardiac Sciences today.