What is Lobectomy?
Lobectomy, a type of partial lung resection, is a surgical procedure where one lobe of the lung is removed. The lungs are divided into sections called lobes, with the right lung consisting of three lobes and the left lung having two. Lobectomy is commonly performed to treat conditions such as lung cancer, infections, and other lung diseases.
Lobectomy is often recommended for patients with early-stage lung cancer, where the cancer is confined to one lobe. It can also be a treatment for other conditions like tuberculosis, fungal infections, or benign tumors. The primary goal of a lobectomy is to remove the diseased or damaged part of the lung to prevent the spread of infection or cancer and improve overall lung function.
Types of Lobectomy
There are three main types of lobectomy
Open Lobectomy
This traditional approach involves a thoracotomy, where the surgeon makes a large incision in the chest to access the lungs. The ribs are spread apart to allow the surgeon to remove the affected lobe
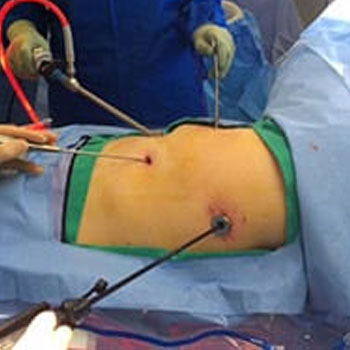
Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS) Lobectomy
This minimally invasive technique uses small incisions and a thoracoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a camera and surgical instruments) to perform the surgery. VATS lobectomy is associated with less pain, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery compared to open lobectomy
Robot-Assisted Lobectomy
This advanced technique uses robotic arms controlled by the surgeon to perform the surgery with high precision. Robot-assisted lobectomy combines the benefits of minimally invasive surgery with enhanced dexterity and visualization, allowing for complex procedures to be performed more effectively
Indications for Lobectomy
Lobectomy is typically indicated for the following conditions
Lung Cancer
For non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that is localized to one lobe, lobectomy is often the preferred treatment to achieve complete removal of the tumor
Infections
Severe infections such as abscesses or tuberculosis that do not respond to antibiotics may require lobectomy to remove the infected tissue
Benign Tumors
Although benign tumors are non-cancerous, they can sometimes grow large enough to cause symptoms and may need to be surgically removed.
Congenital Malformations
Structural abnormalities present at birth can sometimes necessitate lobectomy for improved lung function
What is The Procedure of Lobectomy?
Before the surgery, patients undergo a thorough evaluation including imaging studies like CT scans, PET scans, and pulmonary function tests to assess lung health and determine the best surgical approach.
During the Surgery
- Anesthesia: The patient is placed under general anesthesia.
- Incision: Depending on the type of lobectomy, the surgeon makes an appropriate incision
- Lobe Removal: The affected lobe is carefully dissected from the surrounding tissue and blood vessels. Special attention is given to preserving the remaining lung tissue
- Closure: The incision is closed with sutures or staples, and a chest tube is placed to drain fluids and help re-expand the lung
Recovery and Postoperative Care
Recovery time varies depending on the type of lobectomy performed. Patients typically spend several days in the hospital, especially after an open lobectomy. Minimally invasive techniques like VATS or robot-assisted surgery usually result in shorter hospital stays
Postoperative Care
- Pain Management: Pain relief is crucial for recovery. Medications are administered to manage pain and discomfort
- Breathing Exercises: Patients are encouraged to perform breathing exercises and use incentive spirometry to prevent complications such as pneumonia and to promote lung expansion
- Follow-Up: Regular follow-up visits are essential to monitor healing, lung function, and to check for any signs of complications or recurrence of disease
Lobectomy is a crucial surgical intervention for various lung conditions, particularly lung cancer. With the evolution of minimally invasive techniques, the procedure has become safer and recovery times have shortened. If you or a loved one is facing a diagnosis that may require lobectomy, it is essential to consult with a thoracic surgeon to discuss the best treatment options tailored to the specific condition.
For more information about lobectomy and lung health, reach out to your healthcare provider or a specialized pulmonologist.