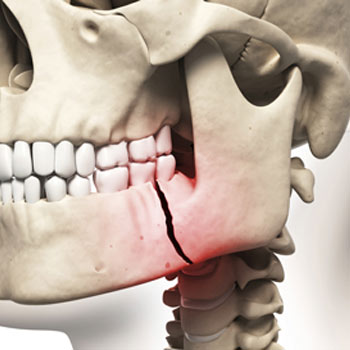
What is Maxillofacial Trauma?
Maxillofacial trauma, also known as facial trauma, refers to any injury to the face or jaw. This type of trauma can result from various incidents, including car accidents, falls, sports injuries, physical assaults, and workplace accidents. Maxillofacial trauma encompasses a wide range of injuries, from minor cuts and bruises to severe fractures and soft tissue damage. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of maxillofacial trauma is crucial for effective management and recovery.
Causes of Maxillofacial Trauma
Maxillofacial trauma can be caused by numerous factors, each varying in severity and impact. Common causes include
- Motor Vehicle Accidents: Collisions often lead to severe facial injuries due to the high impact
- Falls: Accidental falls, especially in elderly individuals or children, can cause significant facial injuries
- Sports Injuries: Contact sports such as football, boxing, and hockey carry a high risk of facial trauma
- Physical Assaults: Fights or violent encounters frequently result in facial injuries
- Workplace Accidents: Certain occupations, particularly those involving machinery, carry a risk of facial injuries
Symptoms of Maxillofacial Trauma
The symptoms of maxillofacial trauma vary depending on the type and severity of the injury. Common symptoms include
- Pain: Intense pain in the facial region is a primary symptom
- Swelling: Swelling around the injured area is common and may indicate underlying fractures
- Bruising: Bruising around the eyes, nose, or mouth can be a sign of trauma.
- Deformity: Visible deformities or asymmetry in facial features can indicate fractures or severe tissue damage
- Bleeding: Cuts and lacerations can cause significant bleeding
- Difficulty Breathing: Trauma to the nasal passages can obstruct airflow
- Vision Problems: Injuries near the eyes can cause vision disturbances or loss
Diagnosis of Maxillofacial Trauma
Diagnosing maxillofacial trauma involves a thorough physical examination and imaging tests. Healthcare professionals will assess the extent of the injury through
- Physical Examination: A detailed examination to check for visible signs of trauma
- X-rays: Used to identify fractures in the facial bones
- CT Scans: Provide a more detailed view of the bones and soft tissues to detect hidden injuries
Treatment of Maxillofacial Trauma
Treatment for maxillofacial trauma depends on the severity and type of injury. Common treatments include
- Medication: Pain relievers and antibiotics to manage pain and prevent infection
- Suturing: For cuts and lacerations, suturing is often necessary
- Fracture Repair: This may involve wiring or plating fractured bones to stabilize and allow healing
- Reconstructive Surgery: Severe cases may require reconstructive surgery to restore function and appearance
- Physical Therapy: To regain full functionality, especially in cases involving jaw injuries
Prevention of Maxillofacial Trauma
Preventing maxillofacial trauma involves taking safety precautions in everyday activities. Recommendations include
- Wearing Seatbelts: Reduces the risk of severe injury in car accidents
- Using Protective Gear: Helmets and face guards in sports and certain occupations can prevent injuries
- Fall Prevention: Implementing safety measures in homes and workplaces to prevent falls
- Avoiding Violence: Promoting non-violent conflict resolution strategies to prevent physical assaults
Maxillofacial trauma is a serious medical condition that requires prompt attention and appropriate treatment. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help in managing the condition effectively. Prevention through safety measures and protective gear is crucial in reducing the incidence of facial trauma. If you suspect maxillofacial trauma, seeking immediate medical attention is essential to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.