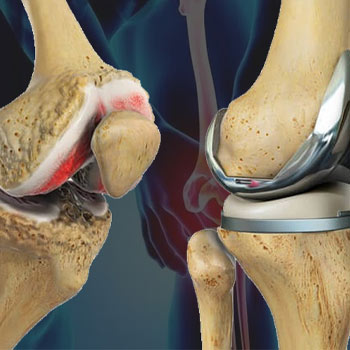
Total Knee Replacement (TKR), also known as total knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure aimed at relieving pain and restoring function in patients with severe knee joint damage. This damage may result from conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or traumatic injury. As a significant orthopedic intervention, TKR involves replacing damaged or diseased knee joint surfaces with artificial components made of metal and plastic. This article aims to provide a detailed overview of TKR, covering its indications, procedure, recovery process, potential complications, and outcomes
What are the indications for total knee replacement?
TKR is typically recommended for individuals whose knee joint functionality has significantly deteriorated due to
Osteoarthritis
A degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone
Rheumatoid Arthritis
An autoimmune disorder causing inflammation and joint damage
Post-Traumatic Arthritis
Arthritis that develops following a severe knee injury or fracture
Other Conditions
These may include avascular necrosis, where bone tissue dies due to reduced blood supply, and certain knee deformities
Candidates for TKR often experience persistent knee pain that limits daily activities, severe joint stiffness, and reduced mobility despite conservative treatments such as medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
What is involved in the Total Knee Replacement Procedure?
Preoperative Evaluation
Before undergoing TKR, patients undergo a thorough evaluation, including
- Medical History Review: Assessing overall health status, previous surgeries, and current medications
- Physical Examination: Evaluating knee joint range of motion, stability, and strength
- Imaging Studies: X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans to assess the extent of joint damage
Surgical Procedure
TKR surgery generally involves the following steps
- Anesthesia: Administering either general anesthesia (where the patient is unconscious) or regional anesthesia (where only the lower body is numbed).
- Incision: Making an incision over the knee to access the joint
- Bone Reshaping: Removing damaged bone and cartilage surfaces from the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shin bone)
- Implant Placement: Affixing metal implants to the newly prepared bone surfaces, with a plastic spacer inserted between them to facilitate smooth movement
- Patellar Resurfacing: Sometimes, resurfacing the undersurface of the patella (kneecap) to improve joint alignment
- Closure: Closing the incision with sutures or staples
The entire procedure typically takes a few hours, but actual surgical time may vary based on individual circumstances
What is the process of recovery and rehabilitation?
Hospital Stay
Following TKR, patients usually stay in the hospital for a few days. During this time, they receive pain management medications, antibiotics to prevent infections, and physical therapy to regain knee mobility and strength
Post-Hospital Care
Once discharged, recovery continues at home with emphasis on
- Physical Therapy: Regular exercises to improve knee flexibility, strength, and overall function
- Pain Management: Medications as prescribed to manage post-operative pain and discomfort
- Wound Care: Keeping the surgical incision clean and monitoring for signs of infection
- Activity Modification: Gradual return to daily activities with restrictions on heavy lifting and high-impact exercises
Potential Complications
While TKR is generally safe, complications may include
- Infection: Risk minimized with antibiotics and sterile surgical techniques
- Blood Clots: Managed with medications and compression stockings.
- Implant Problems: Rare instances of implant loosening, fracture, or dislocation
- Nerve or Blood Vessel Damage: Potential but uncommon risks during surgery
What are the expected outcomes?
TKR surgery aims to alleviate pain and improve knee function significantly. Most patients experience
- Pain Relief: Reduction in knee pain that allows for increased mobility
- Improved Function: Enhanced ability to perform daily activities like walking, climbing stairs, and bending
- Longevity: TKR implants can last 15-20 years or more with proper care
Total Knee Replacement surgery is a transformative treatment option for individuals suffering from severe knee joint damage due to arthritis or injury. By replacing damaged knee joint surfaces with prosthetic components, TKR aims to relieve pain, restore function, and enhance overall quality of life. While it involves surgical risks and requires diligent post-operative care and rehabilitation, the benefits often outweigh the challenges for eligible candidates. If you or someone you know is considering TKR, consult with a qualified orthopedic surgeon to discuss individualized treatment options and expectations.
In summary, Total Knee Replacement surgery represents a significant advancement in orthopedic care, offering renewed hope and mobility to countless individuals worldwide.